A Visual Guide to CAD

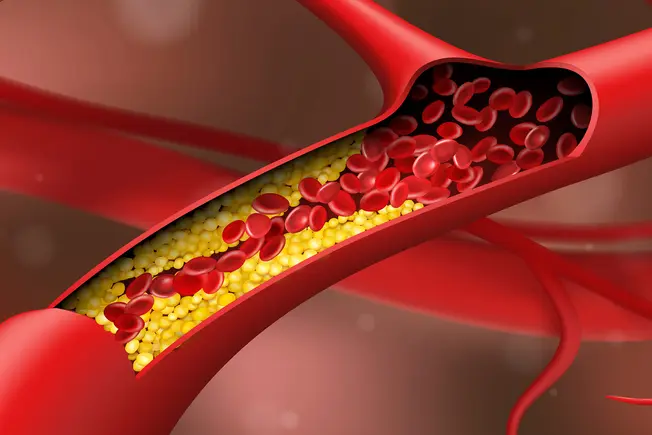
What Is CAD?
CAD stands for coronary artery disease. When you have it, blood flow through your arteries to your heart slows down or even stops. That means the blood can’t carry oxygen to your heart muscles. This can damage your heart, cause chest pain, like angina, or even lead to a heart attack.
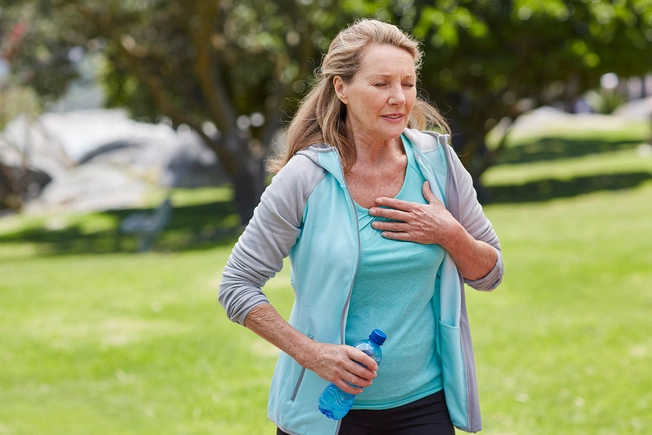

Does CAD Have Symptoms?
CAD often causes no symptoms early on. You may not know you have it until you have a heart attack. Angina and shortness of breath are the only early symptoms. Angina is chest pain or tightness, usually triggered by activity or stress.
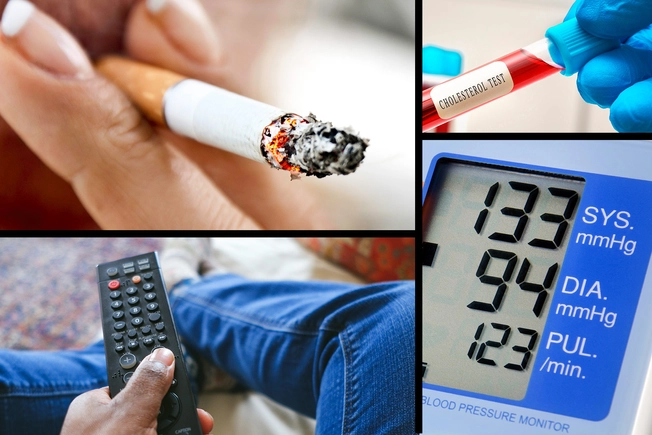

What Causes CAD?
CAD can happen if your arteries are damaged or weakened over time. This can be brought on by smoking, high cholesterol, diabetes, high blood pressure, or lack of exercise. High blood cholesterol can form plaque -- fatty buildup inside your arteries. Over time, plaque can narrow arteries or block them, causing a heart attack.
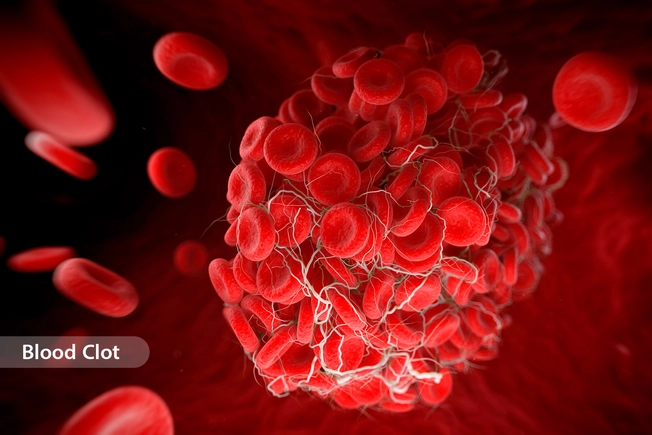
Does Inflammation Play a Role in CAD?
Smoking, high cholesterol, diabetes, and high blood pressure cause inflammation that weakens and damages blood vessels. Ongoing inflammation causes plaque to form, build up, and break off into clots that cause heart attacks or strokes.

What Are the Risk Factors for CAD?
Older age and family history raise your risk of CAD. People who are Black or South Asian are also at higher risk. Other risk factors are things you can try to manage, including smoking, physical inactivity, obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, diets high in saturated or trans fats and salt, and stress.
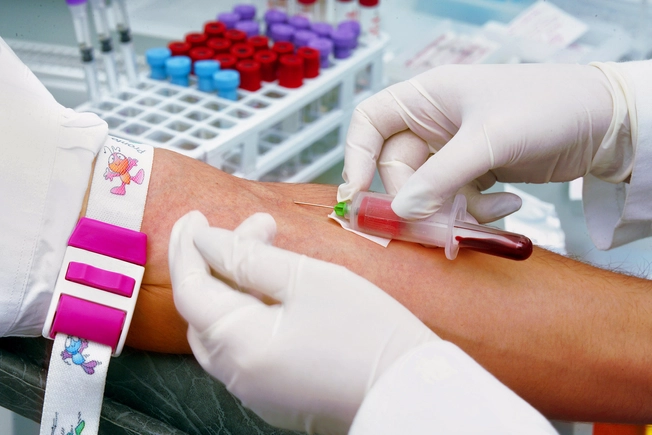
How Is CAD Diagnosed?
Your doctor will do a physical exam and ask about your medical history. They may do blood tests to check for high cholesterol and other possible signs. CT scans can see if there are lots of calcium deposits inside arteries, a sign of CAD. They may need to inject contrast dye into your artery to get a more detailed scan.
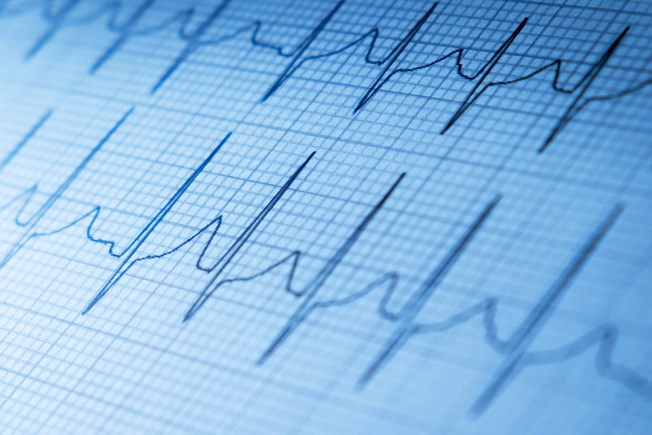

What Heart Tests Help Diagnose CAD?
An electrocardiogram (EKG) tests your heart’s electrical signals to check for damage. Echocardiograms use your heart’s sounds to create images of blood flow and force, valves, and muscles to detect damage or weakness. Exercise stress tests measure heart function as you walk on a treadmill. Nuclear stress tests use fluid injected into your bloodstream to track blood flow on a screen.
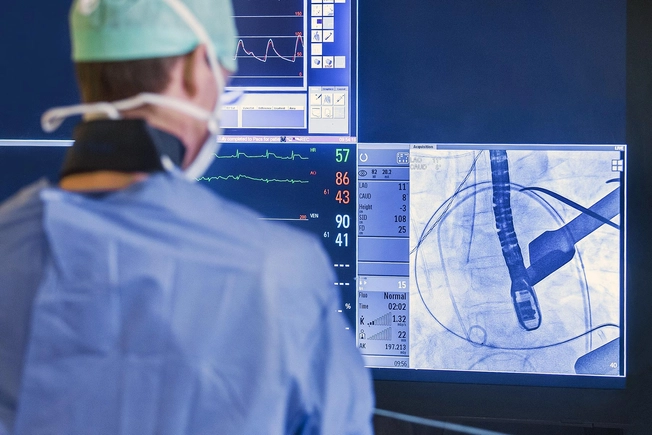
What Is Cardiac Catheterization?
Cardiac catherization is a procedure to check heart function or look for blocked arteries. A long catheter tube is put into an artery or vein in your leg or groin to track your blood flow. Dye injected through the catheter can show how blood flows through your arteries and spot any blockages.
How Can Medications Help Treat CAD?
Medications can work in several ways: Some help improve blood flow and reduce the risks of clots, and others help ease angina pain. Your doctor may also prescribe cholesterol-lowering drugs like statins, blood pressure medicine, or anticoagulants or daily aspirin to prevent blood clots.
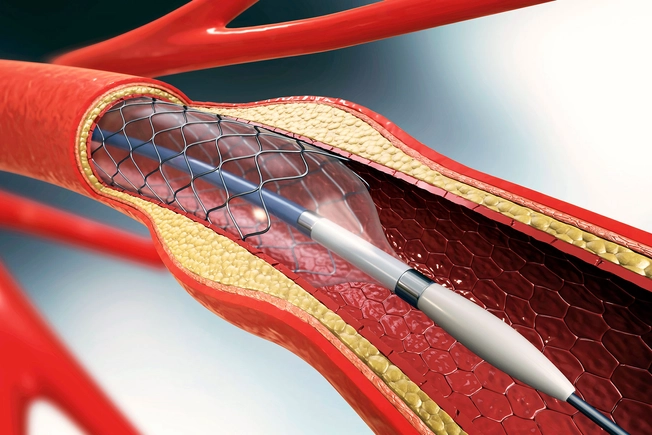
Are There Surgical Treatments for CAD?
If you have a narrowed or blocked artery, your doctor may do a procedure called a balloon angioplasty. A tiny balloon is inserted into your coronary artery through a catheter to open the vessel. They can also insert a stent, a tiny device to hold open your artery. Bypass surgery can reroute blood flow by inserting segments of arteries or veins to bypass the blocked arteries.
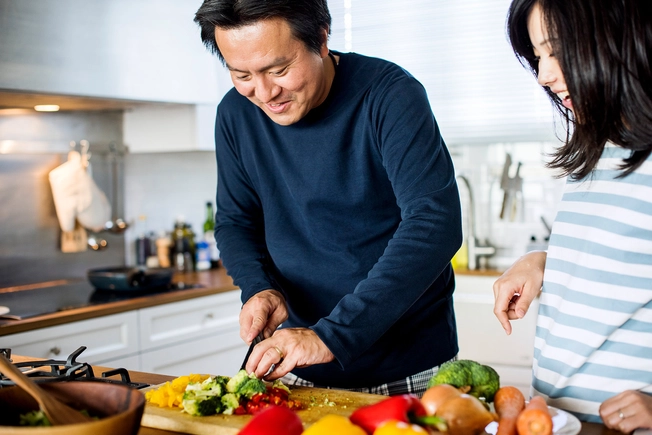

Will Lifestyle Changes Help?
Healthy lifestyle changes can help you manage CAD. Eat a healthy diet, get regular exercise, and if you smoke -- quit. Try to lose weight if you’re overweight or obese. And find ways to reduce and manage your stress.

Can CAD Be Prevented?
Healthy lifestyle changes help prevent CAD. Eat a healthy diet, exercise, quit smoking, and manage your stress and your weight. If you drink, drinking alcohol in moderation can help reduce plaque in your arteries. If you have conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes, make sure you are managing them well.
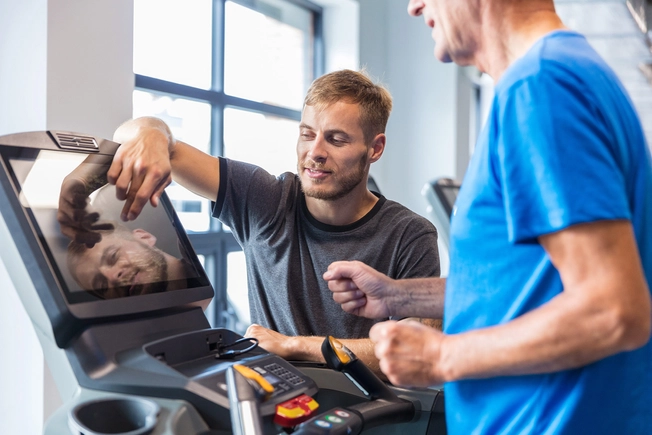

Living With CAD
Follow your treatment plan and take your medications as prescribed. Try cardiac rehab to learn how to manage symptoms and to exercise safely. Living with CAD can sometimes trigger depression. Counseling can help you manage your feelings.